Functions
This tutorial will walk you through creating functions and calling them using exec.
Although normal triggers execute when certain guild events happen, functions can only be triggered manually. There is also a higher limit to the number of functions you can create - 20 by default versus 3 for every other trigger type.
Create
Before you can use exec, you first need to create a function that you can call. To do this you can use the /create-trigger command and select “Function (exec)” for its type. Then you can specify the code just as you would for other trigger types.
Function (exec) is a special type of trigger. Not only can you have more of them (20 versus the normal 3), but they must be triggered manually through a call to exec. When the code executes, its context is derived from the caller’s context. This means it inherits the same triggering user, channel, message, etc. On top of this, it provides a new context input: context.ExecData. This allows the calling code to pass custom data into the function.
Exec
Here is the type signature for the exec function:
exec function data (delay)
Executes a trigger from the Function category. function should be the name of the function as a string (case sensitive). data can contain information you want to pass to the function which will get placed into its context.ExecData entry. delay is optional and can be left out. It is measured in seconds, with a max of 60.
If delay is either left out or set to 0, exec calls the function immediately and returns whatever the function returns (if anything). Otherwise it schedules it to run later and returns empty (nil).
Example: Exec
First create a Function trigger:
/create-trigger name:time type:Function (exec)
Then for the code you can use:
// currentTime is a builtin function
{{$calledAt := currentTime}}
{{respond "Called time"}}
{{return (printf "Called at time %s" $calledAt)}}You’ll notice that we are using printf to create a string that we can return which includes the timestamp. This will allow the calling code to receive data from the function and make use of it.
You’ll also notice that it calls respond. This is a special case where, if the function is called from within a slash command with a delay of 0, it can freely make use of respond as if it were called directly by the slash command. Successive calls to respond will overwrite the initial response data.
Now we can create a new slash command:
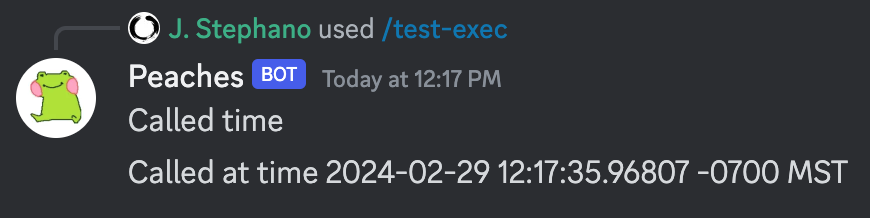
/create-cmd name: test-exec description: Tests the exec function
Command execution code:
// Calls "time" function with empty (nil) data
{{$val := exec "time" nil}}
// Send a new message - we could also use respond
{{sendMessage context.Channel.ID $val}}Here is what it could look like:
You could experiment with adding a delay to the exec call. What you would notice is that it would immediately return and you would get an empty (nil) output.
Example: Exec with delay
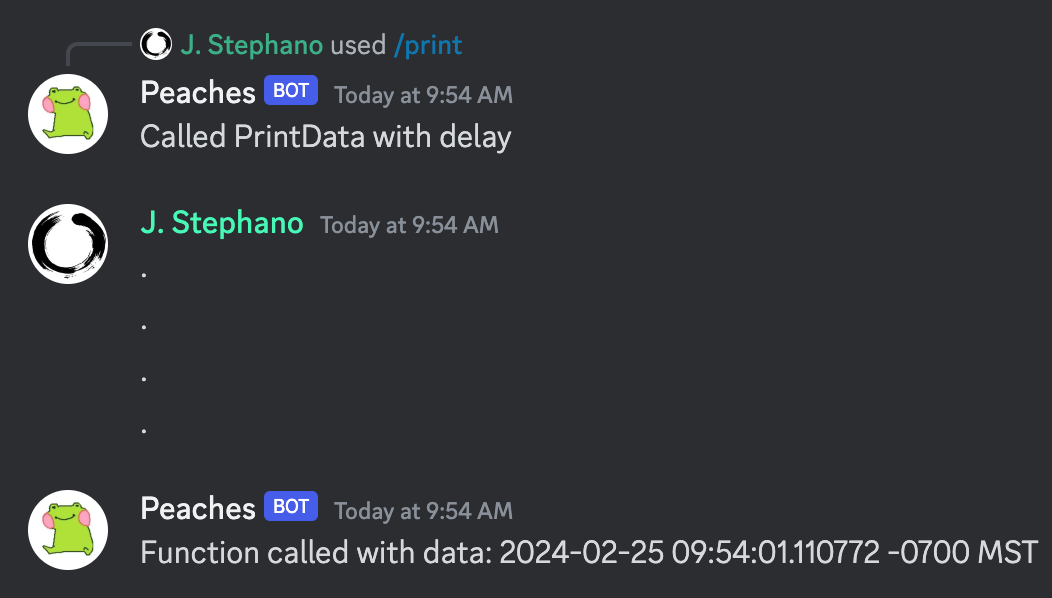
/create-trigger name:PrintData type:Function (exec)
Then for the code you can use:
// Custom input will be placed into context.ExecData
{{$data := context.ExecData}}
// We inherit the channel from caller
{{sendMessage context.Channel.ID (print "Function called with data: " $data)}}Then we create a slash command that will call it:
/create-cmd name: print description: Tests the exec function with delay
Command execution code:
// Add 5 second delay
// currentTime is a builtin function
{{exec "PrintData" currentTime 5}}
// We could also call it with nil if we wanted to
// {{exec "PrintData" nil 5}}
{{respond "Called PrintData with delay"}}Here is what it could look like: